Microfluidic Toolbox for Biology and Biotechnology
- Home
- Research
- Research
- Microfluidic Toolbox for Biology and Biotechnology
Time-resolved Cryo-EM sample preparation for biochemical kinetics
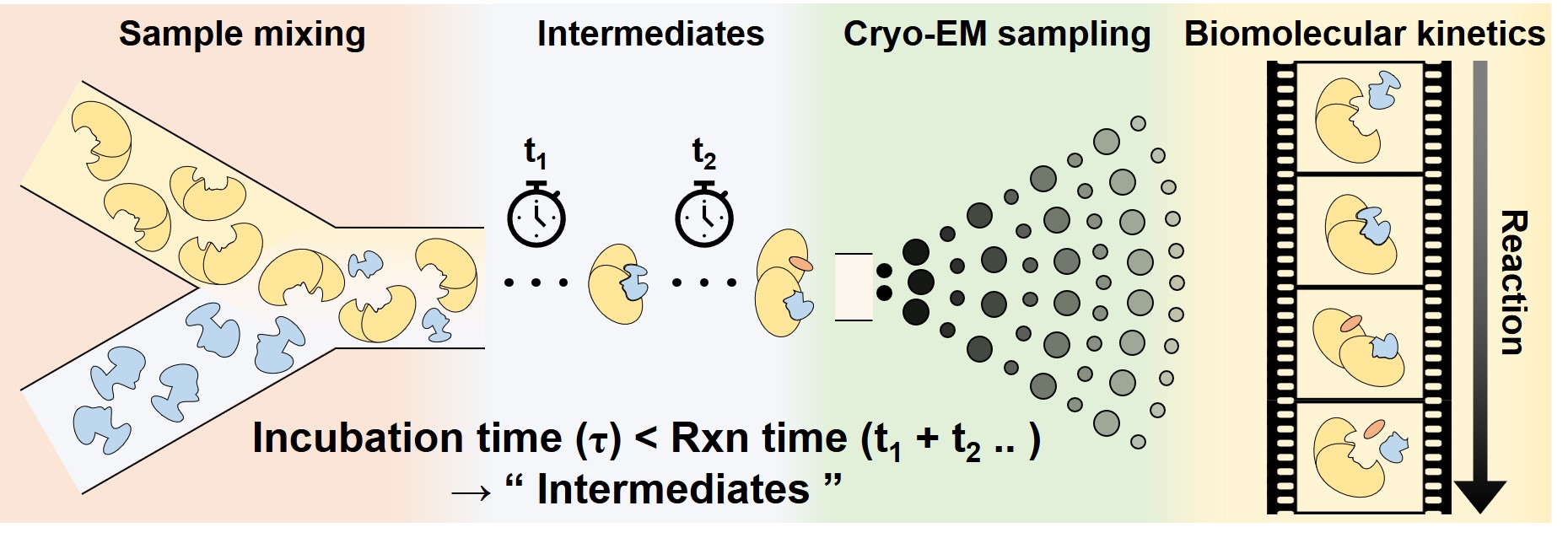
- We developed a time-resolved sample preparation technique for studying biochemical kinetics. Time-resolved Cryo-EM provides precious structural insights for a better understanding of biochemical reactions. The sample preparation technique includes a rapid and complete mixing taking less than 3.4 ms and direct sample spraying on EM grids. The biochemical reactions are quenched by freezing into liquid ethane, resulting in the fixation of the biomolecular structures. We control the time-resolution in a wide range from 20 ms to 1500 ms which targets the majority of biochemical reactions. [Link]
- 시분해 초저온투과전자현미경 분석을 위한 미세유체기반 샘플링 장치를 개발하였습니다. 시분해능 기반의 초저온투과전자현미경 분석법은 생화학 반응을 더 잘 이해할수 있도록 하는 귀중한 구조적 통찰을 제시합니다. 샘플링 장치는 3.4 ms 이내 빠르고 완전한 혼합을 유도하며 EM 그리드에 적용을 위해 스프레이 분사 장치를 통합하였습니다. 생화학 반응의 중단 및 구조적 고정을 위해 90 K (섭씨 영하 183도)의 액화 에탄에서 급랭을 진행합니다. 대부분의 생화학 반응을 대상으로하는 20 - 1500 ms 의 넓은 시분해능 범위를 가지며 이를 조절하여 생화학 반응의 구조적 분석을 수행합니다.
Scalable static droplet arrays for biochemical analysis
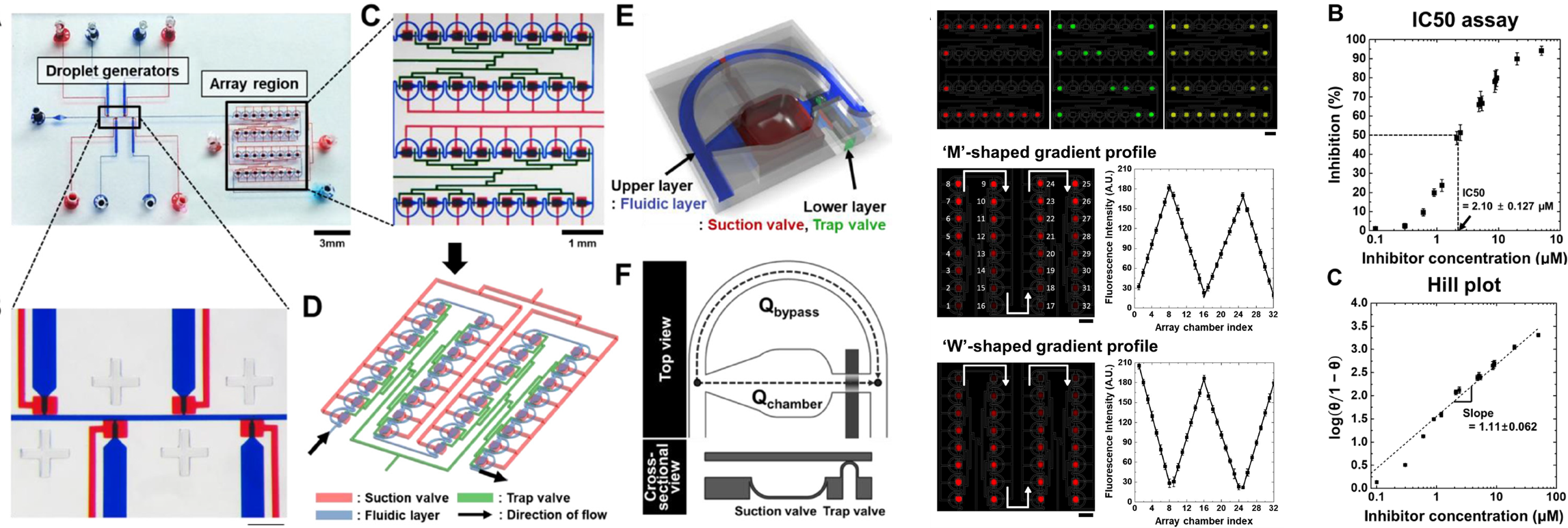
- We present a scalable static droplet array (SDA) that can generate a high-resolution concentration gradient. The system consists of discrete sample dispensing channels, array units, and micro-valves for droplet generation and droplet storage. The size of the droplets is controlled by valve actuation time, and array chambers can contain up to 32 droplets with a 20-millisecond valve actuation time. We present various profiles of concentration gradients generated by the combined storage of binary concentrations of droplets. [Link]
- 높은 해상도를 갖는 농도 구배 액적을 형성하기 위한 액적 어레이 시스템을 제시하였습니다. 이 시스템은 액적을 생성하고 저장하기 위한 독립적인 구조를 갖추고 있으며, 장치 내 존재하는 공압식 밸브를 이용하여 작동합니다. 어레이의 최대 해상도를 향상시키기 위해 액적 어레이가 저장되는 공간의 부피를 확장하고, 액적의 크기를 최소화하여 32단계의 농도를 동시에 구현할 수 있는 장치를 확보하였습니다. 이를 증명하기 위해, β-galactosidase, FDG, PETG를 통한 효소저해 반응을 통해 문헌치에 부합하는 IC50 값과 Hill 상수를 얻을 수 있음을 확인하였습니다.
Monitoring cell-cell interactions in static droplet arrays (SDA)
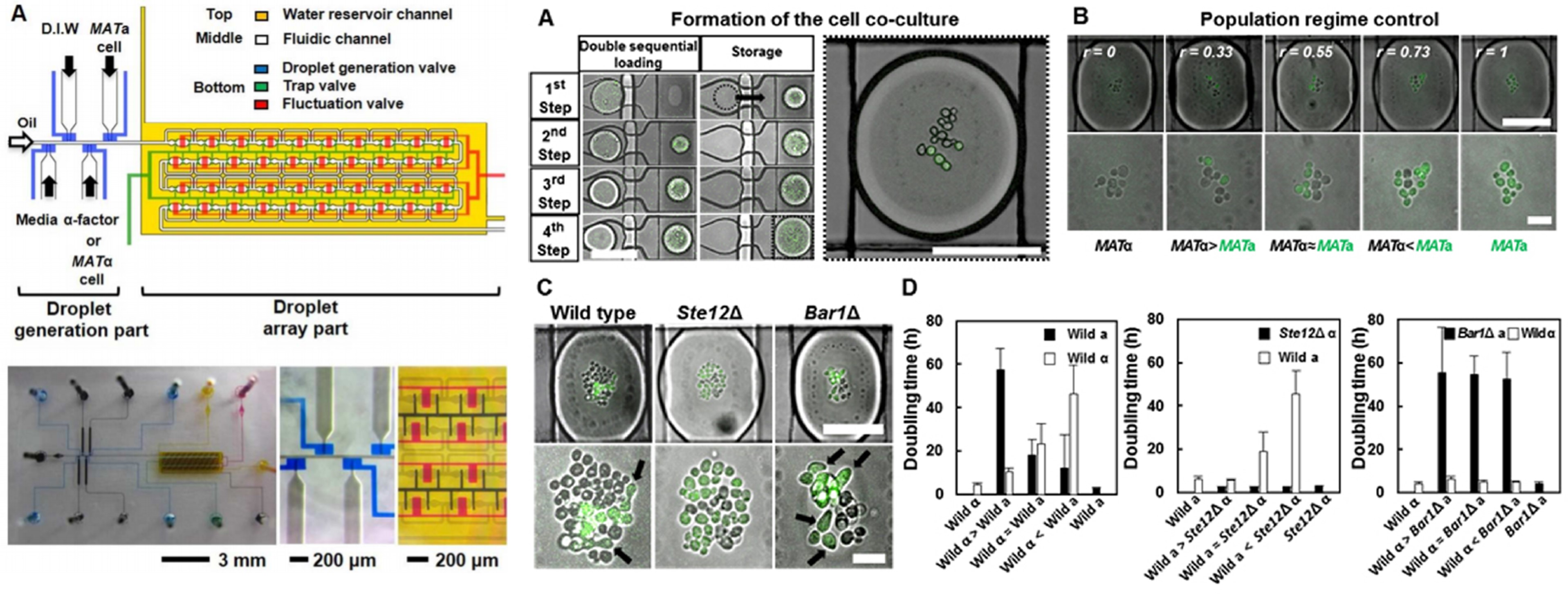
- Direct cell–cell communication can occur through various chemical and mechanical signals. We present an accurate, efficient and controllable microfluidic device that can be used for in situ monitoring of natural cell–cell contact and signaling processes in a confined microenvironment. This innovative static droplet array (SDA) enables highly efficient trapping, encapsulation, arraying, storage, and incubation of defined cell populations. We monitored the response of budding yeast to peptide mating pheromones, as it is one of the best understood examples of eukaryotic cell–cell communication.[Link]
- 세포와 세포 사이의 직접적인 소통은 다양한 화학적 및 물리적 신호에 의해 발생합니다. 우리는 제한된 미세 환경 내에서 실시간으로 세포 간 접촉 및 신호 과정을 모니터링할 수 있는 정확하고, 효율적이며, 제어 가능한 미세유체 장치를 제시합니다. 이 혁신적인 정적 액적 어레이는 정의된 세포 집단을 효율적으로 포획, 캡슐화, 배열, 저장 및 배양을 가능하게 합니다. 진핵 세포 간 소통의 대표적인 예로서, 우리는 펩타이드 짝짓기 페로몬에 대하여 발아하는 효모의 반응을 관찰하였습니다.
High productive E.coli sorting in static droplet arrays (SDA)
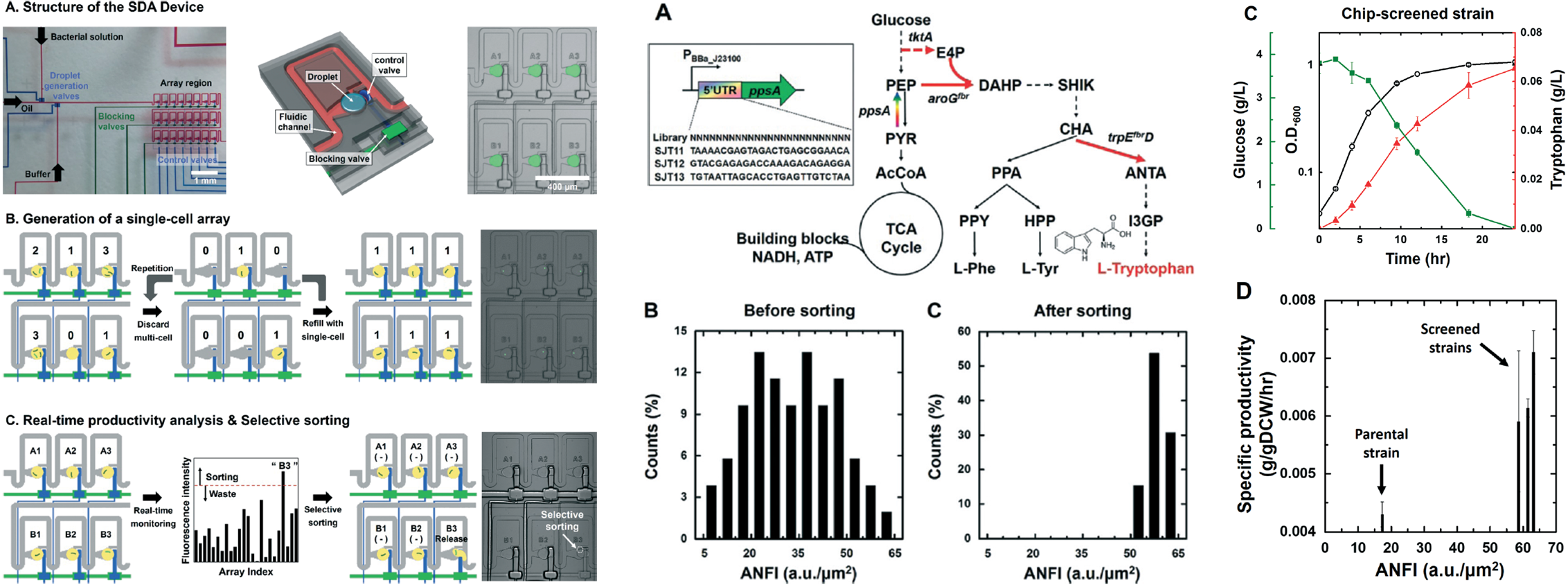
- We established a screening platform that couples a microfluidic static droplet array (SDA) and an artificial riboswitch to analyse intracellular metabolite concentration from single microbial cells. We entrapped single Escherichia coli cells in SDA to measure intracellular L-tryptophan concentrations. It was validated that intracellular L-tryptophan concentration can be evaluated by the fluorescence from the riboswitch. [Link]
- 단일 미생물로부터 세포 내 대사산물의 농도를 분석하기 위해, 미세유체 기반의 정적 액적 어레이(SDA)와 riboswitch를 결합한 스크리닝 플랫폼을 개발하였습니다. 세포 내 L-트립토판의 농도를 측정하기 위하여 우리는 단일 대장균 세포를 각 SDA 내에 포획하였습니다. 이를 통해 세포 내 L-트립토판의 농도는 riboswitch로부터 발생한 형광에 의해 평가될 수 있는 것을 확인하였습니다. 이 시스템을 이용하여 높은 L-트립토판 생산량을 가지는 대장균 균주를 확보하기 위해 염기서열 중 UTR 부분에 무작위적 염기서열 변화를 부여한 변이주 라이브러리를 제작하고 이를 스크리닝 하였습니다. 결과로 얻어진 균주들은 기존 균주에 대해 45%가량 향상된 생산성을 가지는 균주를 선별할 수 있음을 증명하였습니다.
Monitoring quorum sensing with gradient droplets
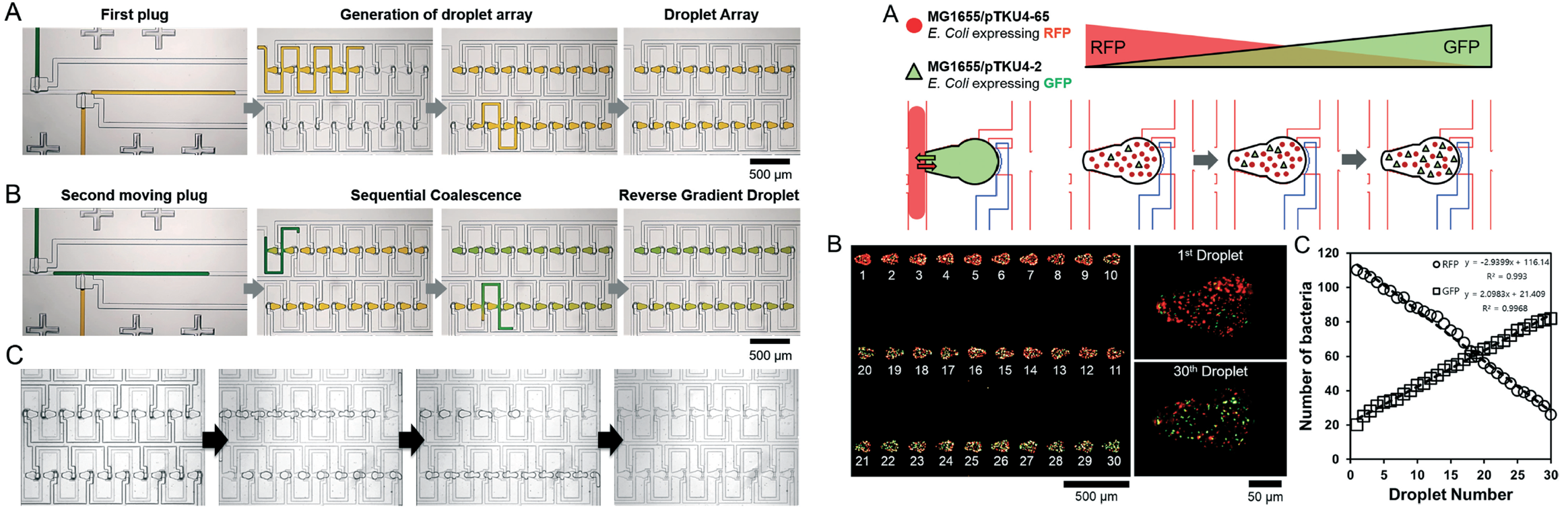
- Quorum sensing (QS) is a type of cell–cell communication using signal molecules that are released and detected by cells, which respond to changes in their population density.We present a microfluidic static droplet array (SDA) that combines a droplet generator with hydrodynamic traps to independently generate a bacterial population gradient into a parallel series of droplets under complete chemical and physical isolation. we found that the population ratio of the signal sender and receiver indicates a significant and potentially interesting partnership between microbial communities. [Link]
- Quorum sensing은 세포에 의해 방출되고 감지되는 신호 분자를 통한 세포 간 소통 중 하나로, 이는 세포 집단의 밀도 변화에 반응합니다. 우리는 화학적 및 물리적으로 완전히 격리된 일련의 액적에 세균의 농도 구배를 형성하기 위하여 유체역학적 트랩과 정적 액적 어레이를 결합하였습니다. 이를 통해 우리는 신호 발신자와 수신자의 비율이 미생물 공동체 간의 중요하고 잠재적으로 흥미로운 협력 관계를 나타내는 것을 발견하였습니다. 이 시스템은 다양한 미생물 공동체 내에서 발생하는 생물학적 현상에 대한 이해를 향상시키는데 기여할 수 있을 것으로 생각합니다.
Monitoring chromosome dynamics of budding yeasts in cell trapping arrays
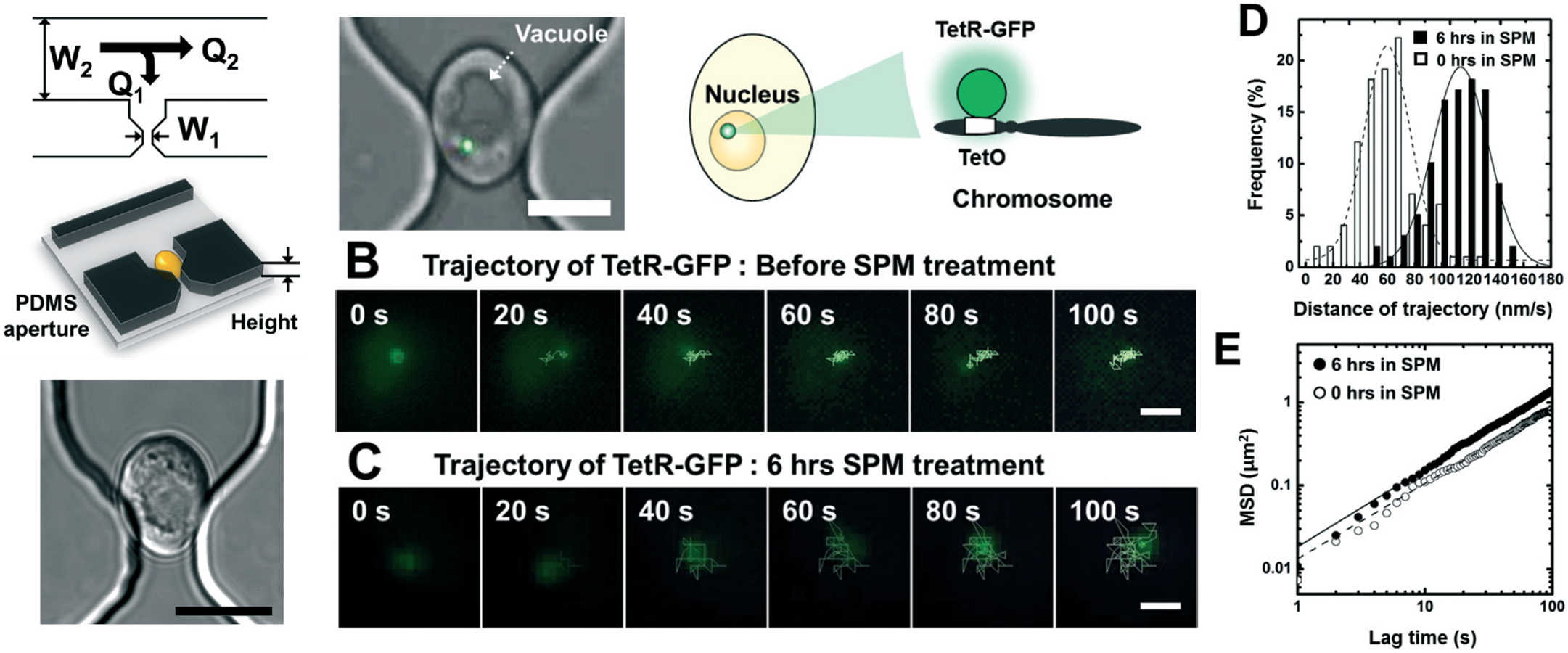
- We present a simple microfluidic platform with aperture-based cell trapping arrays to monitor the chromosome dynamics in single living cells for a desired period of time. This microfluidic approach enables in situ imaging of intracellular dynamics in living cells responding to variable input stimuli under the well-controlled microenvironment. We investigate the fundamental features of the dynamic cellular response of the individual cells treated with different stimuli and drug. We prove the basis for dynamic chromosome movement in single yeast cells to be the telomere and nuclear envelope ensembles that attach to and move in concert with nuclear actin cables. [Link]
- 살아있는 세포 내 염색체의 동역학적 관찰을 위한 미세유체 플랫폼을 제시하였습니다. 단일 효모세포의 효율적인 포획을 위해 조리개와 같은 작은 aperture를 제작하고 단일 세포를 포획하였습니다. 이러한 방법은 살아있는 세포 내에서 외부 자극에 대한 변화를 실시간으로 관찰하는 것을 가능하게 합니다. 우리는 서로 다른 자극 및 약물에 의해 처리된 개별 세포들의 동적 세포 반응의 기본적인 특징들을 조사하였습니다. 이를 통해 우리는 단일 효모세포에서 pachytene 염색체의 움직임이 액틴케이블과 텔로미어/ 핵막의 회합을 필요로 함을 확인하였습니다.
Monitoring bacterial chemotaxis with pumpless microfluidic device
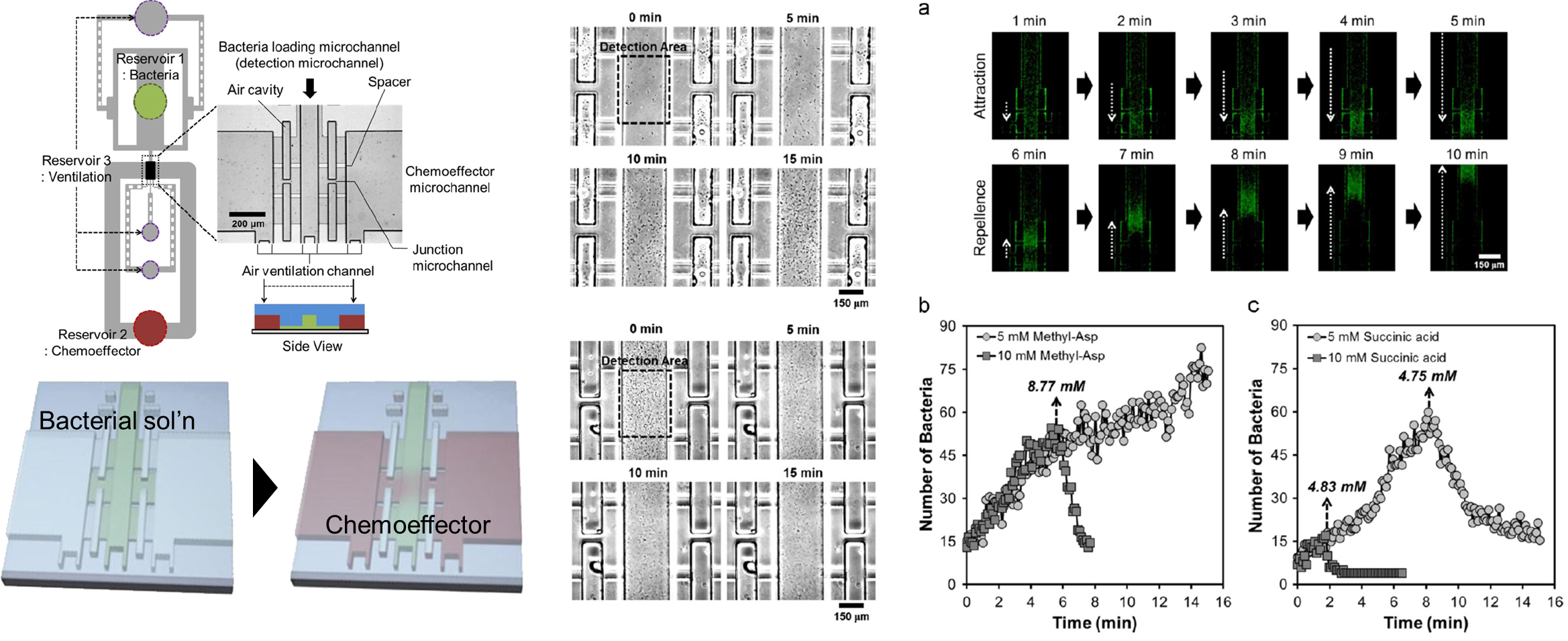
- We present a diffusion-based microfluidic device to provide rapid diffusion of chemoeffectors using a liquid-liquid interface, which is a critical advance in the analysis of bacterial chemotaxis. The microfluidic method can rapidly analyze attractants and repellents, achieving a chemotaxis index corresponding to the concentrations and types of chemoeffectors. Moreover, we find that the dynamic switch in bacterial chemotaxis from attraction to repellence in response to specific chemoeffectors occurs in a concentration-dependent manner. [Link]
- 미생물은 화학물질에 반응하여 움직임을 보이는 현상인 주화성을 가집니다. 최적화된 미생물의 주화성 연구를 위해 제어된 환경 내에서 박테리아와 농도 구배를 부여할 수 있는 장치를 제작하였습니다. 농도 구배 부여를 위한 유체공급장치가 필요한 기존 미세유체장치의 문제점을 해결하기 위해, 모세관력을 이용한 자동적인 농도 구배를 형성하고 이에 따른 박테리아의 움직인 변화를 분석할 수 있도록 했습니다. 알려진 Chemoeffector들을 사용하여 박테리아의 움직임이 알려진 형태와 동일하다는 것을 확인하였고, 비교적 잘 알려지지 않은 현상으로 농도 구배가 커짐에 따라 특정 농도 이상에서 박테리아의 운동 방향이 변화하는 현상을 확인할 수 있었습니다.
Profiling surface glycans of live cancer cells
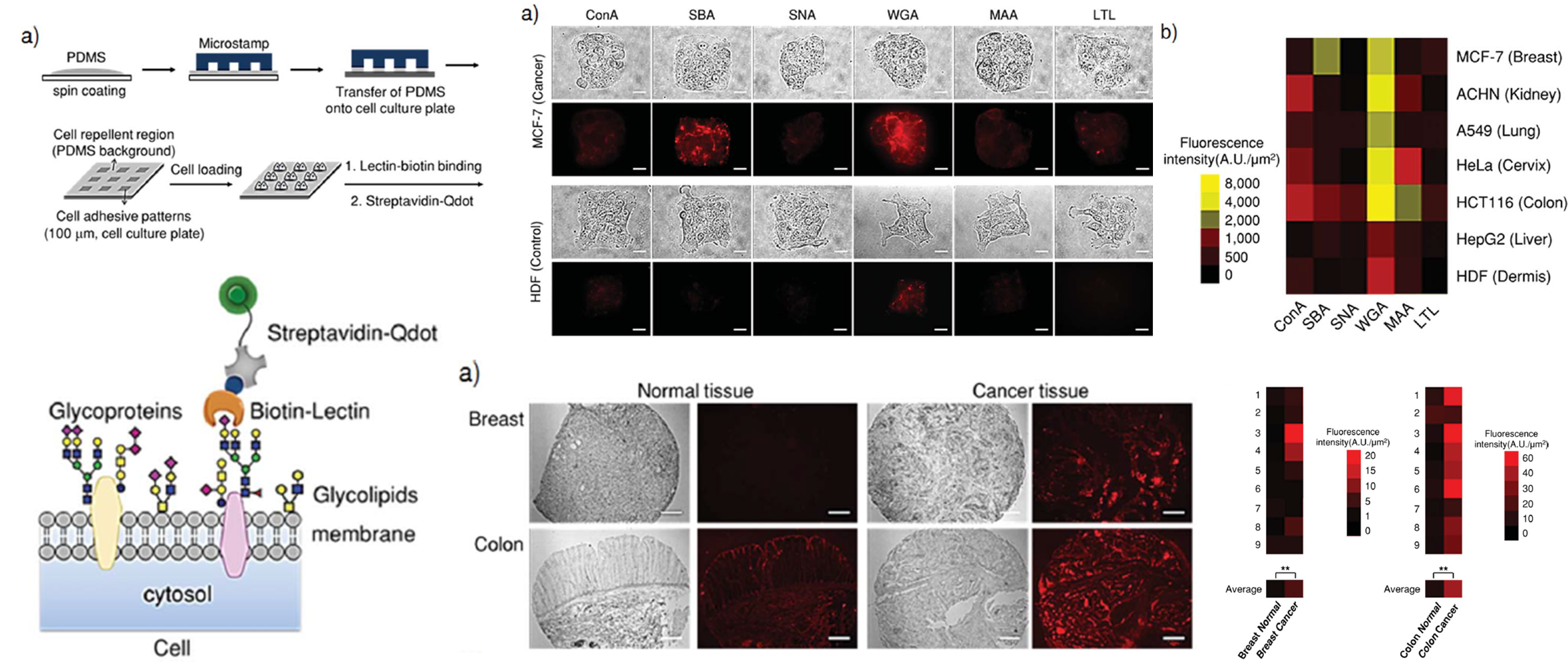
- We present a novel glycomics approach that uses quantum dot (Qdot)-lectin nanoconjugates to interrogate the surface glycans of tissues and patterned cells. Our approach allows highly sensitive in situ monitoring of specific lectin–glycan interactions and quantitative information on surface glycans for each examined cell line and tissue. The results clearly show significant changes in glycosylation for each cell line and tissue sample. [Link]
- 세포의 표면에 존재하는 당사슬은 세포의 종류, 세포의 상태 등을 확인할 수 있는 물질입니다. 우리는 세포의 표면에 존재하는 당사슬을 손쉽게 분석하기 위해 세포 패터닝 기술과 세포 표면 결합 물질인 lectin을 활용한 기술을 개발하였습니다. Lectin의 종류에 따라 세포 표면의 당사슬과 결합할 수 있는 능력이 달라지며, 형광 발광을 일으키는 퀀텀닷 (Quantum-Dot) 입자를 표지하였습니다. 이를 이용하여 암세포의 종류에 따른 세포 표면 당사슬을 분석할 수 있음을 확인하였습니다.











